Textile Dryer Machine:
In wet processing industry, textile dryer machine is used after de-watering of fabric. Drying machine is used for removing the residual water contained in the fabric after squeezing by applying heat on the fabric. In this machine the fabric is fed on the drying net at low over feed speed and the humidity is continuously measured. Drying process in textile industry is done by applying heat through burner nozzles. During drying the total heat passed through the machine is extracted by the exhaust fan. In textile finishing unit; dryer uses for dry the knit, woven fabrics and dyed yarn. We can define drying as a process where the liquid portion of the solution is evaporated from the fabric. In this article I will discuss about dryer machine and its drying process in textile industry.

Objects of Drying Machine:
- To dry the fabric with help of steam
- To remove residual water containing in the fabric
- To control the shrinkage
- To prepare for next subsequent process
- To dry tubular and open width fabric without tension
Dryer Machine Specification:
|
Tensionless Dryer Machine |
|
| Manufacturer name | Lk and LH.Co |
| Country | Taiwan |
| Heating arrangement | Steam |
| Maximum width capacity | 330 cm |
| Used Utilities | Water Electricity, Compressed Air |
| Speed range | 8.8 m/min |
| Heating range | 110-150°C |
| Chamber | 04 |
Table: Machine specification of Tensionless Drying machine
Fabric Path Diagram of Textile Dryer:
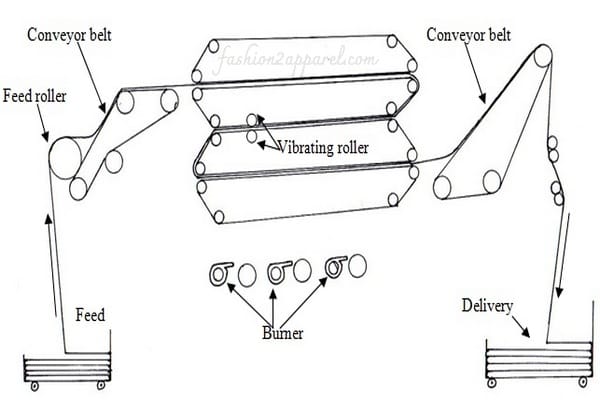
Main Parts of the Dryer Machine:
- Heating chamber (2)
- Blower
- Synthetic blanket as a conveyor
- Folder
- Exhaust fan
Heating Arrangement:
- Heating chamber: 2
- Heating system: Gas fired
Function of Textile Dryer:
- In case of Tensionless dryer, drying of fabric is carried in relaxed/tensionless state, which is suitable for Knitted fabric.
- Two mesh conveyors are placed length wise to the chamber named upper and bottom conveyor and they are endless and made of taflon, under the bottom conveyor there is a vibrator which makes the fabric more relaxed.
- There is a steaming zone which causes more shrinkage of fabric, hot air is circulated by fans .
- To control the shrinkage
- To prepare for next subsequent process
Utility:
- Gas (to make fire)
- Electricity (to rum the machine)
- Compressed air (to spread the fire)
Remarks: If moisture content of air is less, more energy is required to heat up the atmosphere and vice versa. So optimization of moisture of air is needed, by controlling the speed of Fabric or Fan.
Drying Process in Textile Industry:
Drying process is very essential in textile industry to eliminate or reduce the water from the fibers, yarns and fabrics following wet processes. Drying happens when liquid is vaporized from a product by the application of heat. Drying, in particular by water evaporation, is a high-energy-consuming step although overall consumption may be reduced if re-use/recycling options are adopted.
Drying Methods:
Fiber, yarn or fabric can be dried with mechanical or thermal process. Mechanical processes are used in general to remove the water which is mechanically bound to the fiber. This is aimed at improving the efficiency of the following step. Thermal processes consist in heating the water and converting it into steam. Heat can be transferred by means of:
- Convection
- Infrared radiation
- Direct contact
- Radio-frequency
Drying techniques depend on packages. Loose fiber can be dried in three ways:
- Centrifugal extraction
- Mangling
- Evaporative drying
In other way, hanks may be dried by employing a dehumidifying chamber. Moisture is recovered by condensation, using conventional de-humidification equipment. In comparison to evaporative dryers, yarn residence time tends to be longer, but energy consumption is lower.
Yarn Packages Drying:
The moisture of dyed packages is initially reduced by centrifugal extraction. Specially designed centrifuges, compatible with the design of the dyeing vessel and yarn carriers are employed.
Fabric Drying:
The drying process for fabric usually involves two steps: the first one is aimed at removing water which is mechanically bound to fibres, while the second one is necessary to dry completely the fabric.
- Hydro-extraction by squeezing
- Hydro-extraction by suction
- Centrifugal hydro-extractor
- Stenter process
Economic Control of Drying:
Most of the factors affecting the cost of drying processes have already been mentioned, and may be summarized as follows:
- Mechanical removal of water must be maximized, and achieved as uniformly as possible;
- Drying should not proceed beyond the equilibrium regain of the fabric;
- Thermal efficiency of convection drying requires that optimum humidity of the drying medium be maintained;
- Air temperature should be high for speed of drying, but if taken above about 150°C unit costs are usually increased;
- Air velocity at the fiber surface should be maximized – through-flow drying shows a clear advantage here;
- Losses by radiation and in the exhaust should be minimized – steam supply losses should be eliminated by direct heating within the drying chamber.
You may also like: Manufacturing Process of Textile Industry

Editor of Fashion2Apparel. She is a fashion designer and ex-lecturer in Fashion Designing. She wants to spread fashion knowledge throughout the world.
I appreciate you letting us know that drying in the textile industry involves the application of heat through burner nozzles to de-water the fabric and remove residual water. My brother recently invested in a textile mill since he wants to get into the apparel business in the future, so he needs the right equipment for his new business operations soon. I’ll have to mention this to him while he is still looking for an equipment supplier to contact about the textile machinery he’ll be needing soon.