Garment Export Procedure:
Garment industry is one of the largest contributors to the global economy, and exporting garments plays a vital role in international trade. Countries like Bangladesh, India, China, and Vietnam export billions of dollars’ worth of apparel every year. Garments exportation from one country to another, that involves a structured process to ensure compliance with international trade regulations, customs, and buyer requirements.
Normally the documents which are to be submitted by a C & F to the customs authority for exporting goods are called export documents. When garment manufacturers or exporters of garment buying house want to garment goods to other countries they need to prepare export documentation. In this post I have try to give a basic idea about export procedures and formalities for garment. This export process is same in almost all countries with slight variation. I hope this post helps you in getting a basic training on how to export various products.
For exporting apparel goods to the buyer’s country normally following garment export procedure and documentation are required. Now I will explain A to Z guide of the garment export procedure with the key documentation required at each stage.
Garment Export Procedure and Documentation: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide
1. Market Research and Buyer Identification
Identify potential markets and buyers for your garments.
Participate in trade shows, B2B platforms (e.g., Alibaba, IndiaMART), and export promotion councils.
Documents:
- Company Profile
- Product Catalog / Lookbook
- Factory Certifications (e.g., ISO, SA8000, WRAP)
2. Sampling and Product Development
Develop garment samples based on buyer specifications.
Include lab dips, fit samples, size sets, etc.
Documents:
- Tech Pack
- Sample Invoice
- Approval/Feedback from Buyer
3. Pricing and Negotiation
Send pro forma invoice with product details and price.
Negotiate price, Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF), delivery, and payment terms.
Documents:
- Pro Forma Invoice
- Cost Sheet
4. Purchase Order (PO) / Sales Contract
Buyer issues a PO after finalizing price, delivery, and quantity.
Documents:
- Purchase Order
- Contract of Sale (optional but advisable for large orders)
5. Raw Material Sourcing and Production Planning
Procure fabrics, trims and accessories.
Create a Time & Action (TNA) calendar for production.
Documents:
- Material Purchase Orders
- TNA Plan
- Inspection Plan
6. Pre-production Approvals
Obtain approvals for:
- Fabric
- Trims
- Lab tests (shrinkage, colorfastness, etc.)
- Pre-production sample
Documents:
- Pre-production Sample Approval
- Lab Test Reports
- Buyer Approval Emails/Letters
7. Garment Manufacturing
Cut, sew, finish, and pack garments according to buyer specs.
Documents:
- Production Report
- Quality Control Reports
- Packing List (preliminary)
8. Quality Inspection
Conduct final inspection (AQL or buyer’s method).
May involve buyer-appointed inspection agencies (SGS, Intertek, etc.)
Documents:
- Final Inspection Report
- Buyer Approval (if applicable)
9. Shipping and Logistics Arrangements
Book vessel/air cargo.
Decide between FOB, CIF, etc.
Coordinate with freight forwarder or CHA (Custom House Agent)
You may also like: How to Prepare Price Quote for Garment Export Orders
Documents:
- Shipping Instructions
- Booking Confirmation
- Packing List (Final)
- Commercial Invoice
- Declaration of Origin (if required)
10. Export Documentation Preparation
Prepare all documents required for customs clearance, buyer’s requirements, and payments.
Key Documents:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Shipping Bill (filed electronically via ICEGATE in India)
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Certificate of Origin (issued by Chamber of Commerce or Export Promotion Council)
- Export License (if applicable)
- Inspection Certificate (if required)
- GSP Certificate (if exporting under preferential trade agreement)
- Export Declaration Form (EDF) – in India (earlier GR form)
- Insurance Certificate (in CIF shipments)
11. Customs Clearance
Submit documents to customs via CHA.
Pay applicable export duties (usually nil for garments).
Get “Let Export Order” (LEO).
Documents:
- Shipping Bill
- Export Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Other supporting documents
12. Shipment
Cargo is loaded and shipped.
Share tracking and documents with buyer.
Documents:
- Bill of Lading (Original or Seaway)
- Export Invoice
- Packing List
- ETA Details
13. Post-shipment Documents to Buyer/Bank
Depending on payment method (L/C, TT, DA/DP), submit documents to bank or directly to buyer.
Documents:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Certificate of Origin
- Insurance Certificate
- Any other documents as per LC terms
14. Payment Realization
Payment comes via:
- Advance
- Letter of Credit (LC)
- Documents against Payment (DP)
- Documents against Acceptance (DA)
- Open Account
Documents:
- Bank Realization Certificate (BRC)
- Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC)
15. Post-shipment Compliance and Incentives
Submit documents to DGFT and Customs for export incentives like:
- Duty Drawback
- RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products)
- MEIS (discontinued in some countries)
Documents:
- BRC
- EDI Shipping Bill
- Proof of Exports
- GST Refund Application (if applicable)
16. Record Keeping and Audit
Maintain all export documentation for 5–7 years for audits by:
- Customs
- GST Authorities
- DGFT
- Internal/External Auditors
Summary of Export Documents
| Document | Purpose |
| Pro Forma Invoice | Initial quote to buyer |
| Purchase Order | Buyer’s confirmation of order |
| Commercial Invoice | Final invoice for customs/payment |
| Packing List | Details of shipment contents |
| Bill of Lading / Airway Bill | Shipping document |
| Certificate of Origin | For trade preferences/customs |
| Inspection Certificate | Quality assurance (if required) |
| GSP Certificate | Preferential duty claim |
| Shipping Bill | Export declaration to customs |
| BRC / FIRC | Proof of payment |
Documentation may vary slightly by country and buyer, so exporters should verify requirements with relevant government and trade authorities before exporting. This procedure ensures compliance with regulations and smooth cross-border garment export transactions.
At a glance following documents are required for export garments:
1. Invoice
- Commercial invoice
- Consular invoice
- Customs invoice
2. Packing list
3. Certificate of Inspection
4. Certificate of Origin
5. GSP
6. IEC Certificate
7. Wearing Apparel Sheet
8. Bill of Lading
9. Airway Bill
10. Mate’s Receipt
11. Shipping Bill/Bill of Export (for Customs)-
- For export of goods Ex. Bond
- For export of duty free goods
- For export of dutiable goods
- For export of goods under claim of drawback
- For export of goods under claim of DEPB
12. Letter of Credit
13. Insurance
14. UD (Utilization Declaration)
15. VBF- QA from to supply by the C and F agents
16. Export Permission from EXP
Some Important processes are shortly described in below:
Bill of Lading (B/L):
An evidence of contract between the shipper of the goods and the carrier. The customer usually needs the original as proof of ownership to take possession of the goods.
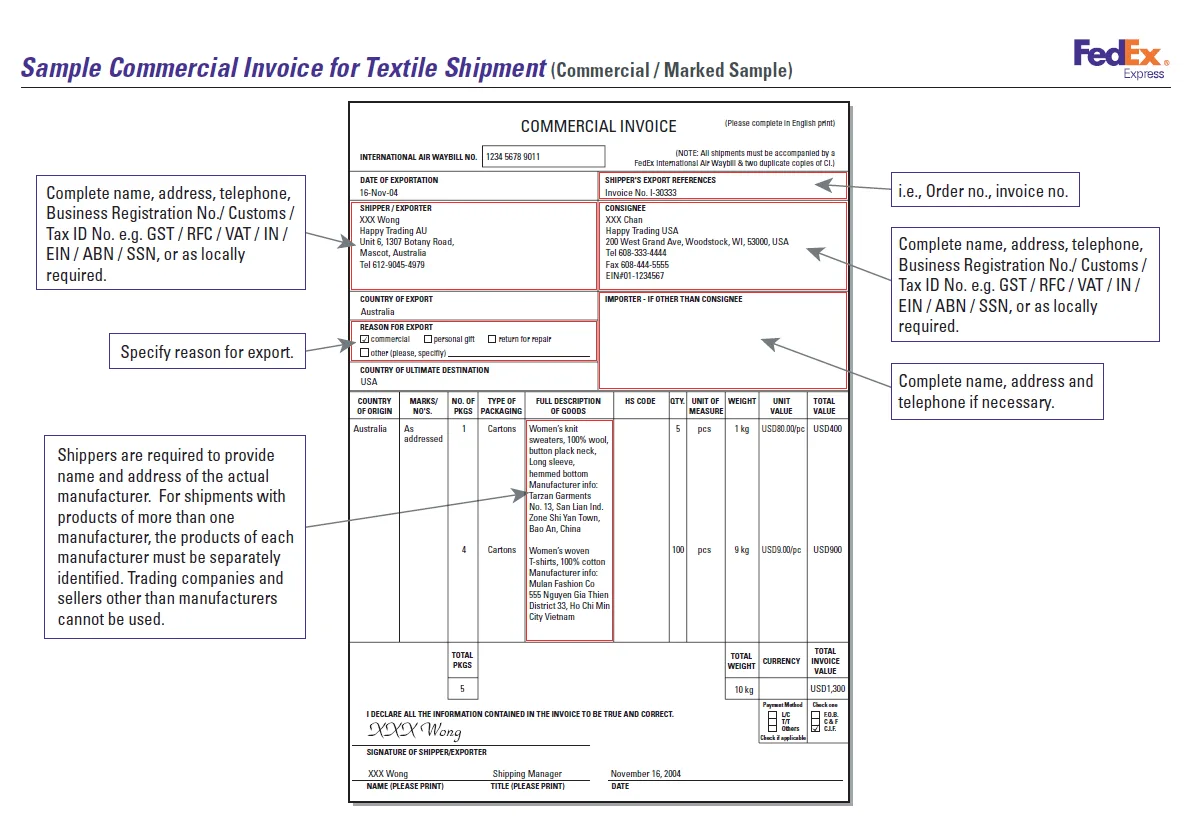
Invoice:
Commercial invoice is a key document in the international trade. In addition to playing an essential role in the commercial transaction, it has an important function as a source of information and supporting document for administrative procedures in the importing and exporting countries.
GSP:
GSP means Generalised System of Preferences (GSP), which provides garment manufacturers with duty-free access. Actually, GSP is an instrument by which developed nations help the poorer countries foster more trade.
L/C:
L/C means Letter of Credit. A letter of credit is a document issued by a financial institution, or a similar party, assuring payment to a seller of goods and/or services provided certain documents have been presented to the bank.
This might not be complete list for country. So, you should double check with Govt. official before exporting goods. Because documents may vary country to country.
Conclusion
A well-organized garment export procedure and flawless documentation are crucial for timely delivery and hassle-free payments in the global apparel trade. By following each step carefully and keeping all paperwork in order, garment businesses can expand globally with confidence.

Editor of Fashion2Apparel. She is a fashion designer and ex-lecturer in Fashion Designing. She wants to spread fashion knowledge throughout the world.