Production System in Apparel Industry:
Production system in apparel industry is the way of manufacturing process that converts the fabric into apparel. Apparel production system is an integration of materials handling, production processes, personnel, and equipments that helps to plan the work flow and produce a complete apparel. As with any manufactured product, there are different ways to organize the actual production of garments, according to the type, the amount and the diversity of products to be made. The type of production system in apparel industry is determined by the quantity of production and the required rate of delivery. Their are various apparel production systems which are discussed in this article.

Factors of Apparel Production System:
Apparel production system depends on some factors. They are:
- Company affordability
- Equipment that directly involved with workflow
- Items of finished products
- Machine or floor layout
- Management philosophy
- Materials handling system
- Personnel training
- Production processes
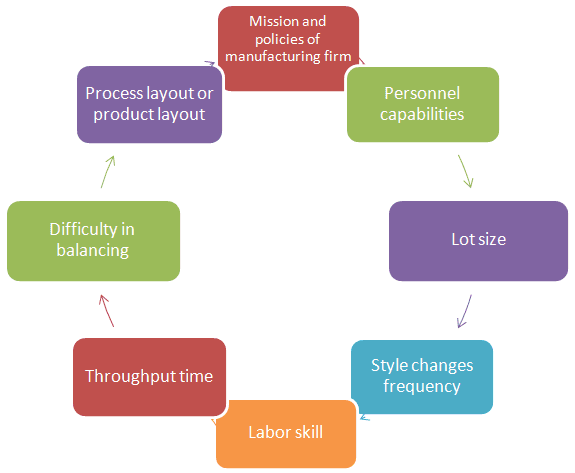
Principles of Choosing a Production System in Apparel Industry:
Types of Production System in Apparel Industry:
There are three main types of apparel production system. According to different ways, they are in below:
- Production systems that are based on order quantity
- Production systems that are based on customer nature
- Production systems that includes on organizational choice
A. Types of production systems that are based on order quantity:
- Individual production or make through system
- Batch production
- Mass production
1. Individual production or make through system:
It is the traditional method. In which the entire garment is assembled by one operator like a tailor. Each product is made only once or in very small quantities. The system requires highly skilled, experienced operator and versatile machinery. In this system tailor do the all jobs like pattern making, fabric cutting, finally finish the garments for completing the garment order. This system also called whole garment production system.
There are two types of whole garment production systems:
- Complete whole garment and
- Departmental whole garment.
2. Batch production:
It is used for larger, though fixed, quantities of identical products either for stock or to order.
3. Mass production:
Mass production means that large quantities of identical products are made continuously. The high utilization of machinery and labor allows a high level of automation and specification.
B. Types of production systems that are based on customer nature:
- Bespoke production
- Industrial production
1. Bespoke Production:
This type of production system is including for individual clients or small group of peoples. A garment is made according to individual size and requirements.
Advantages:
- Cost is low.
- No need of pattern.
- Use one or more number of m/cs.
- Low risk.
Disadvantages:
- Fabric wastage is high.
- More time required.
2. Industrial production:
Industrial production system is use for bulky production, they must follow standard measurement chart and maintain special requirements for target consumer groups.
Advantages:
- Cost is high.
- Low fabric wastage.
- Takes less time.
Disadvantages:
- Pattern must be needed.
- Many machines are required.
- Risk is high.
C. Types of production systems that includes on organizational choice:
- Manual systems
- Mechanical system
1. Manual Systems:
Manual system is the traditional methods of garment production. This type of production system is effectively use for creative garment design and where the style variations are large. In manual system the production quantities are small.
For example – Sewing room of a fashion or boutique house.
Manual systems are divided into 6 types:
a. Section or Processes system:
In section or processes system more skilled operators are needed to sew garment part from beginning to the end. This system includes a small influence of personnel changes and easy style changes. Sewing room has a number of sections; to complete all the operations for every garment component required more versatile operators. When one section ends then it is passed on to the next section. But this system is required more time. This section produce garments according to style. Some working steps are:
- Pre-assembling (preparation of making small parts)
- Front side making
- Back side making
- Main-assembly (closing, setting collar and sleeves,..)
- Lining making
- Setting linings
- Finishing operation
b. Piece rate production system:
In piece rate production system, operators are getting their payment according to their production pieces of garment (how many pieces are they produced). It is one of the most famous production systems for both small and large apparel factories.
c. Clump system:
In the clump system operator collect the garment part from the worktable and start the operation. After finish the work, he returns it to the worktable. A worker for the second operation then continues the work and so on. It is the continuous process until the whole garment has been assembled. This process is work like that
Collection – Work –Return
d. Flexible flow system:
In this system numbers of operators are needed for each operation. Number of machine are arrange according to the flow of work. It can be planned using the accurate number of operations in sequence. For style A garment, operator 1 do his operation one then send it to operator 2. After completing the one and second operations, operator 2 sends the both operation to the operator 3. After operation 3, the work is continued by the two operators performing operation 4 and so on.
e. One piece flow system or Progressive bundle system:
Progressive Bundle System (PBS) is also called one piece flow system or material handling system. It is a traditional production system that widely used in garment manufacturing from early period to still now. After complete the fabric cutting, then various components of fabric parts are to make bundle and distributed to the sewing section. Bundle ticket is attached to cut parts. One operator is tried to perform the same operation on all the parts in the bundle. When one operator finish his/her work then garment bundles are move from other operator. For sewing a garment, numbers of operators are needed. Bundles are handling by the Tied bundles, Bags, Pocketed bags, Boxes and baskets, Bundle trucks, etc
f. Straight-line or Synchro- system:
To do garment manufacturing process, different operations are divided into several parts but the fixed the same time to complete this operation. To complete only one garment group of operators are needed. When one group of operators finish their work then it pass to the next operator. Distribution may be done hand by hand or a conveyor belt.
In synchro- system different garment parts like collars, sleeves, cuffs, pocket etc with the same size, color can be processed together. When all is done then all parts are send central line for assembling a complete garment.
2. Mechanical System:
There are 5 types of production system in the apparel industry.
a. Assembly line production system:
Assembly line production system is mainly planned for a sequential organization. Each operator is appointed only for one operation. Garment parts are move from operator to operator.
b. Overhead production system or Unit Production System (UPS):
For apparel manufacturing, advance mechanical system like overhead production system or unit production system (UPS) is use widely. In this system a single garment is transferred automatically via a computer-controlled overhead handling system to finish the sequence of each operation.
Advantages:
- Automatically move the garment parts from one work place to other work place.
- Use one hanger that contains more clips to hang all the parts of garment.
- Hanging carrier can be moving in both manual and computerized way.
- Time consuming and little work-in-progress.
- Number of machine can be adjusted.
- Increase productivity and improve quality.
- Reduced labor cost.
Disadvantages:
- High investment required.
- Need proper planning.
- Handling equipments are highly expensive.
- Special training required for labor.
c. Selective conveyor belt system:
It is the very common mechanical equipment handling system. In conveyor system automatically feed the materials or working containers to one operator to other. This system is more popular in material handling and apparel manufacturing industries. For saving the time and quick production this system is more effective.
A typical conveyor system is mainly three types:
- Main conveyor
- Top belt
- Lower belt
d. Quick response sewing system:
Quick response sewing system specially use for small lot order. Every work station will assemble with 4-5 machines. Operators are completed their all the operations in that station before it is moved to other work station. If there is a bottleneck in one section, the overload is automatically moved to other stations where operator capacity is available. All the garment parts are hanged on the hanging clamp that attached to the trolley. It is a computer controlled and overhead trolley system.
e. Modular Production Systems (MPS):
In modular production system, group of sewing operators are work together to meet their goal effectively. Usually 4-15 labors are work in one group. Every members of sewing team helps to each other to make a high quality garment. For getting quick production this system is more effective. Multi skilled operators are needed to do this operation. The sewing line layout is set in U –shaped. In modular production system work-in-progress (WIP) is less.
Advantages:
- Flexibility is high.
- Low wastages.
- Employee absence will be low.
- Produce high quality garment.
Disadvantages:
- Equipment price is high.
- Employee training investment is high.
- Team members are depends on each other that affects on production.
Without above three systems of apparel production there are also Individual production system, make through production system, group system, Progressive bundle synchro straight line system – batch system, Unit production system (UPS) etc. The bundle system and PBS are categorized into
mass production and UPS and modular systems are categorized into flexible specialization. Kanakadurga used five attributes of the production systems to classify them in the apparel industry into three categories (i.e., bundle system, PBS, and modular system). Those five attributes are: workflow, method of retrieval between workstations, work in progress (WIP) inventory, number of tasks per operator, and interaction between workers. The study found that one production system could be distinguished from another according to these attributes.
You may also like: Flow Chart and Working Procedure of Finishing Section in Garment Industry

Editor of Fashion2Apparel. She is a fashion designer and ex-lecturer in Fashion Designing. She wants to spread fashion knowledge throughout the world.